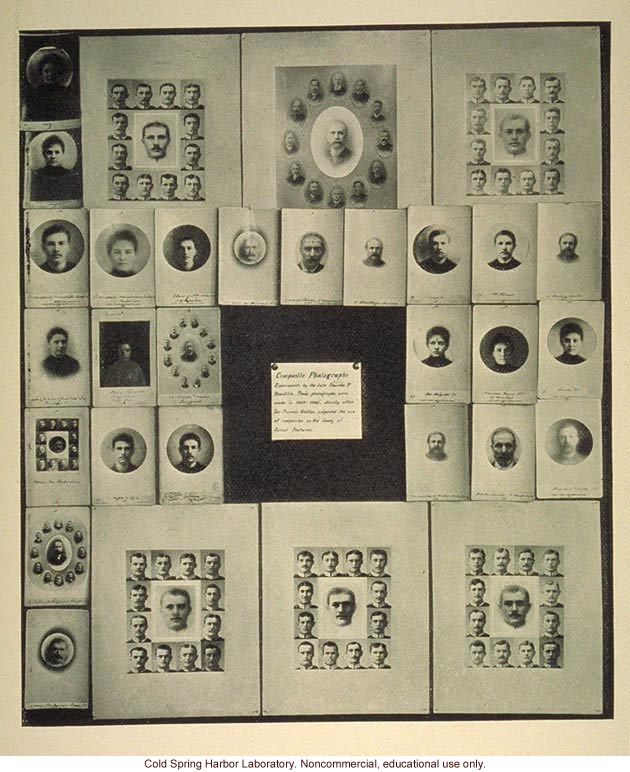

"Composite portraiture," Fig. 35, 1921

Nazi propaganda in Berlin storefront, including anthropometric device for measuring differences between Aryan & Non-Aryan skulls (by Roman Vishniac), 1933
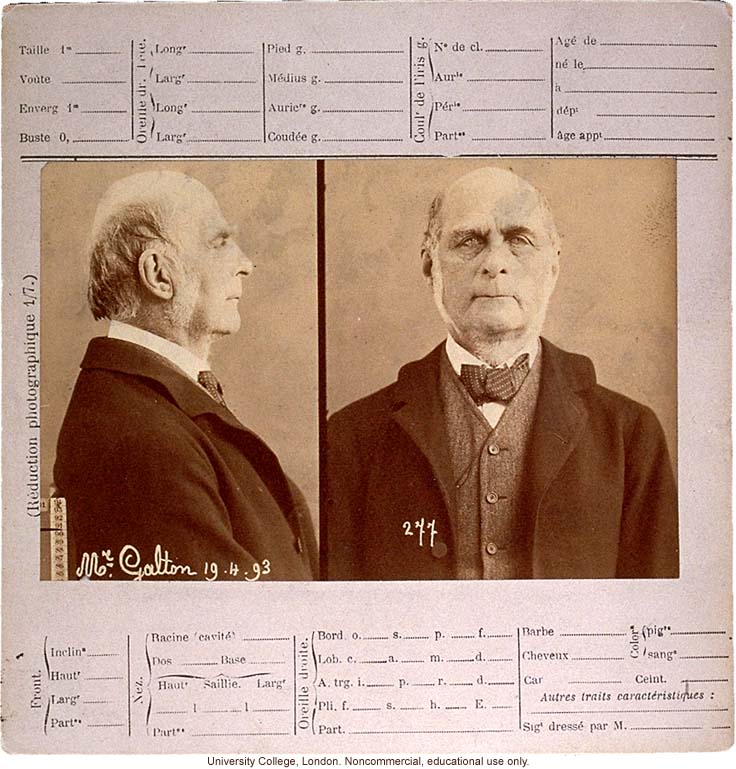
Anthropometry card of Francis Galton, with profile and full-face photos and spaces for key body measurements, taken by Alphonse Bertillon, 1893
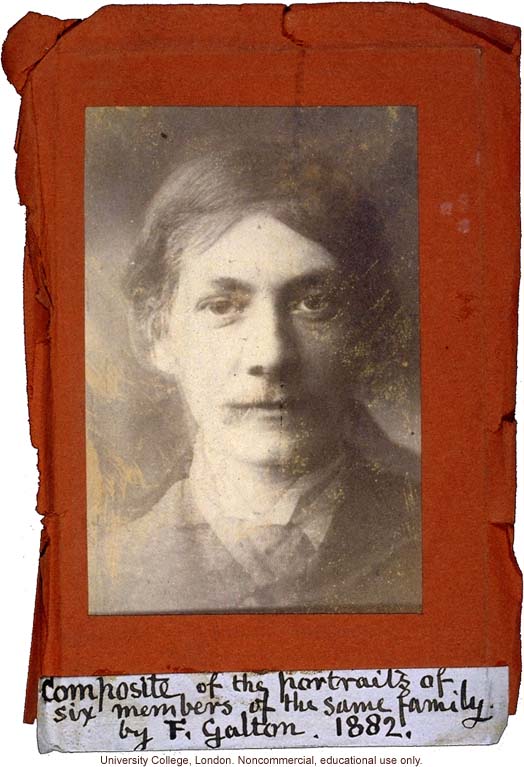

Composite of the portraits of six members of the same family. By F. Galton. 1882.
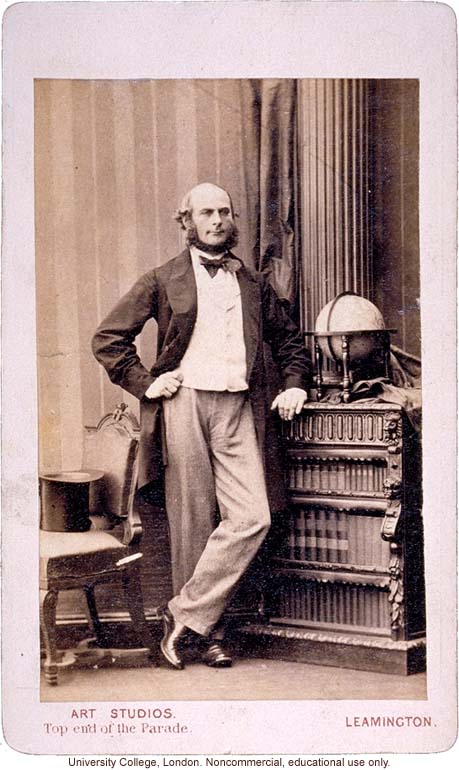

Francis Galton carte de visite portrait, standing, 1864
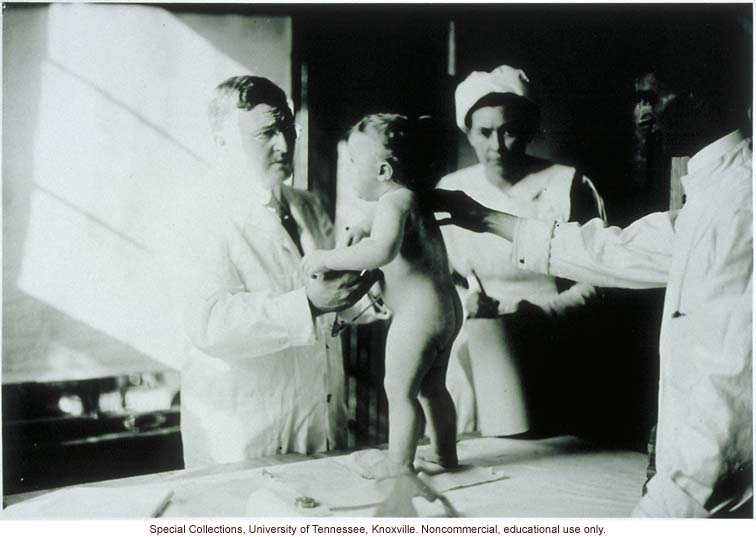
Infant being examined for a Better Babies Contest, 1910
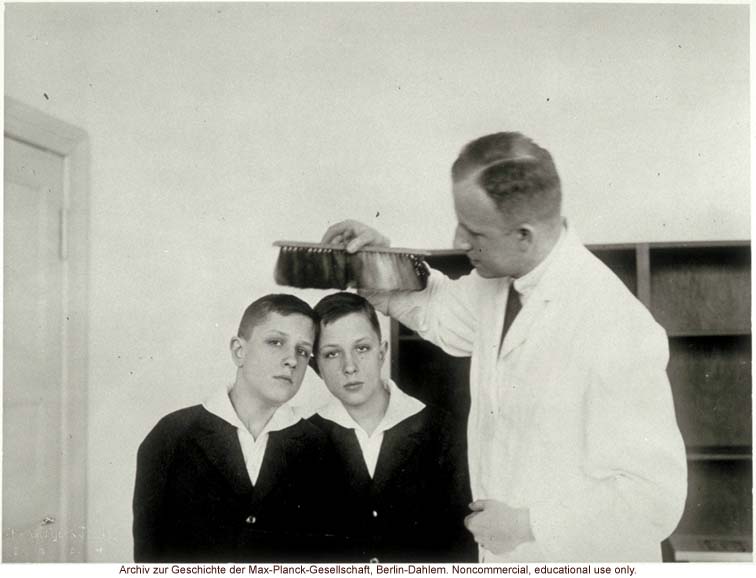
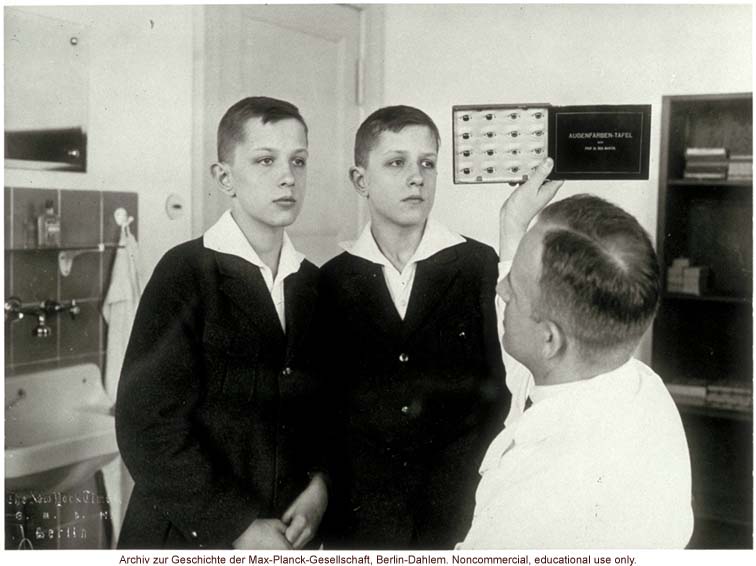

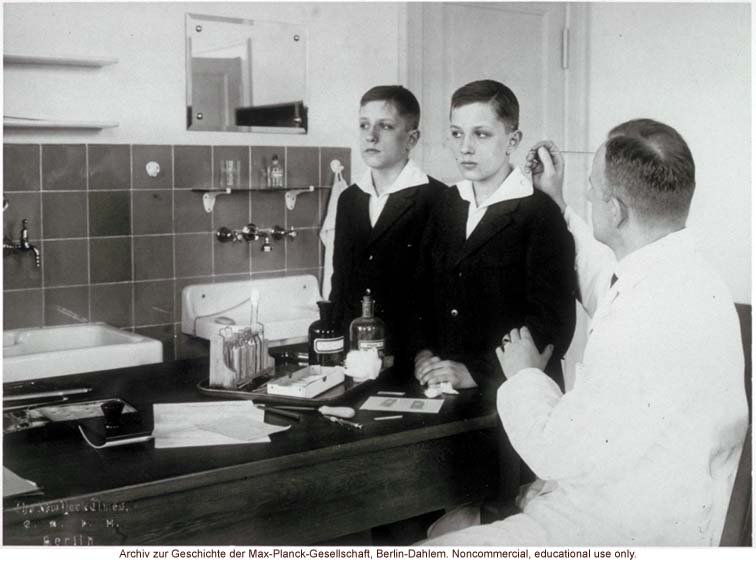
12-year-old male twins undergoing anthropometric study by Otmar Freiherr von Verschuer

Seaford Town female anthropometric case: photos, measurements, finger prints, Schedule 3; by Morris Steggerda for Race Crossing in Jamaica, 1927

Eugenics tree logo, 1925
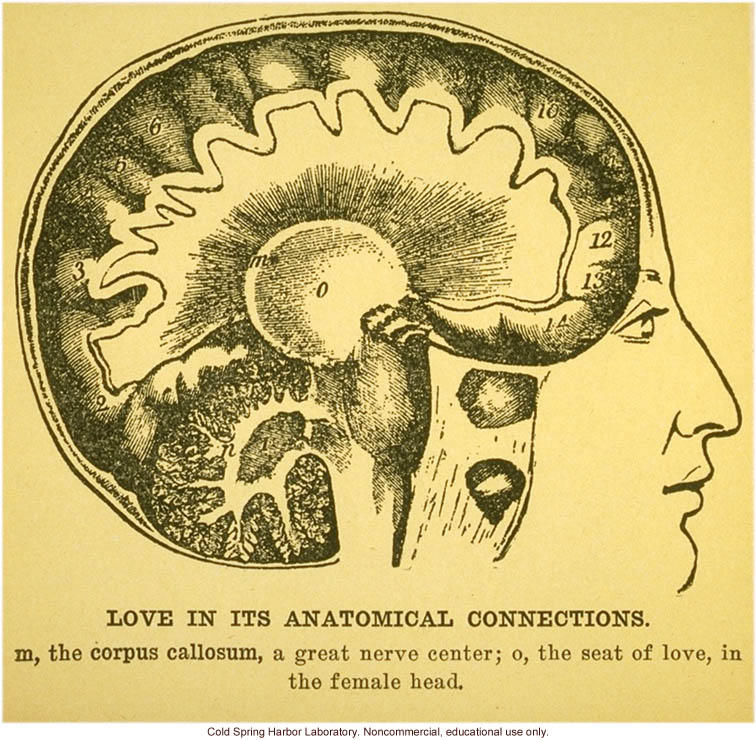
"Love in its anatomical connections", 1930
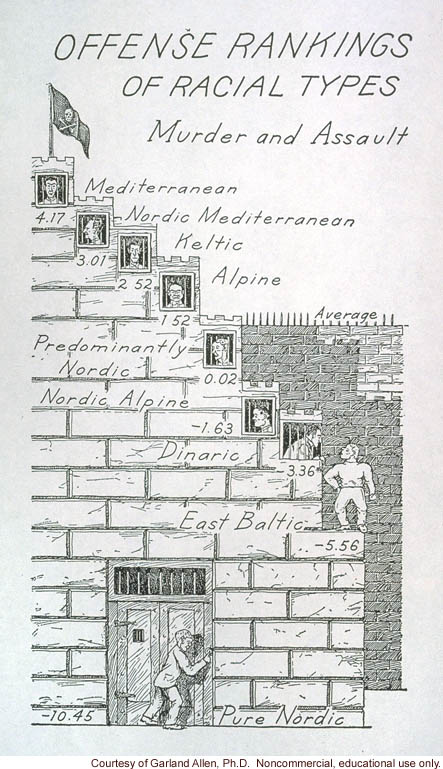
"Offense rankings of racial types: murder and assault"
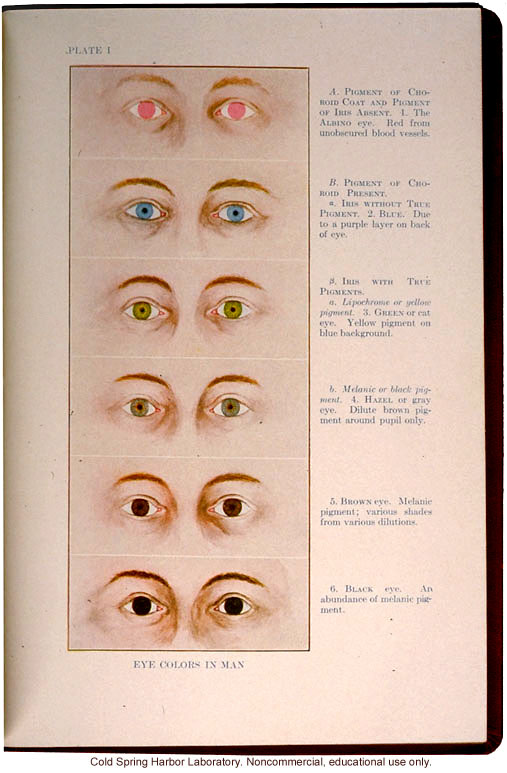
"Eye Colors in Man," from The Trait Book, ERO Bulliten No. 6, by Charles B. Davenport, 1912
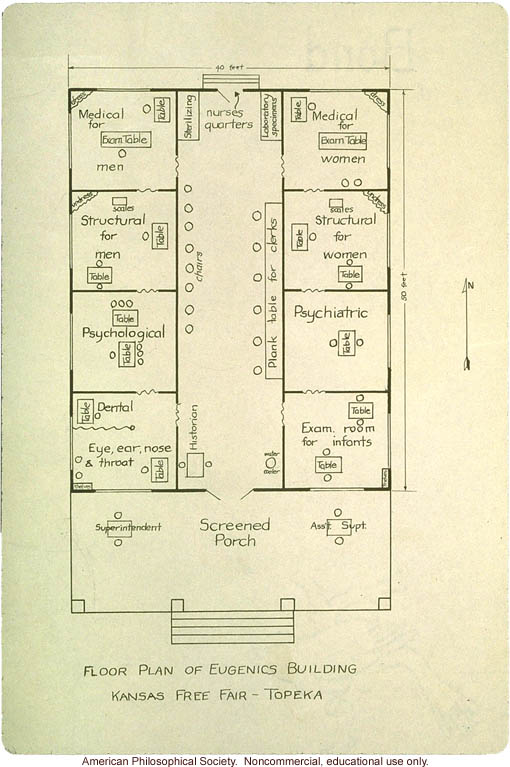
Floor plan Eugenics Building at Kansas Free Fair - Topeka, 1924
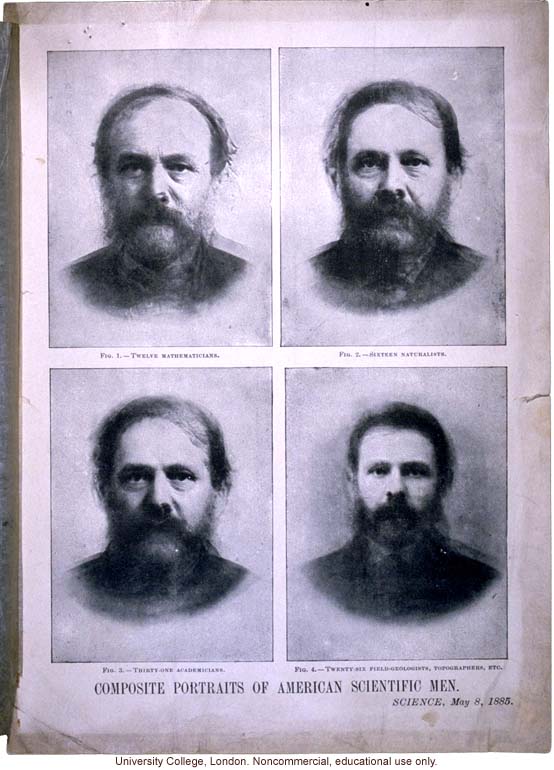

"Composite Portraits of Scientific Men," by Francis Galton, Science (5/8/1885)

"Composite Portraits of Scientific Men," by Francis Galton, Science (5/8/1885)
Francis Galton imbued eugenics with a penchant for measuring all aspects of the human body. Galton relied heavily on the system for human physical measurements (anthropometry) developed by the French criminologist Alphonse Bertillon. Measurements of variation in human form provided much of the data upon which he and his student Karl Pearson developed modern statistics. American eugenicists hoped to use anthropometry to back up their claims about the superiority of the white race and people of northern/western European origin. Public schools, prisons, and mental hospitals all presented large "captive" populations to measure. Draftees into WWI provided a trove of data from which to determine the prototype (White) "American male" to compare to men of other races and ethnicities.
In most cases, it is not clear what point eugenicists were trying to make with their comparisons of body measurements. Apart from athletic prowess, no relationship has ever been shown between bodily measurements and intelligence or other behavioral attributes. Eugenicists also failed to take into account variables — such as differences in nutrition and health care — that could affect human development and account for differences between groups.
Intelligence tests took human measurement to new levels. In 1905, the French psychologist Alfred Binet developed a measure of "mental age" to help steer elementary students to academic or vocational tracks. Under this system, a child of average intelligence has a mental age equal to his chronological age. By 1910, Binet's mental age was used to generate an intelligence quotient or IQ (mental age/chronological age x 100). IQ scores range from 0 to 200 and fit a bell-shaped curve, with an average IQ of 100. Normal intelligence ranges from 86 to 115. Terms like "moron," "imbecile," and "idiot" described persons with IQs below 86, while "bright" and "genius" were used for scores above 115.
Eugenicists rapidly employed IQ or other intelligence tests to compare different racial and ethnic groups. These comparisons purportedly showed whites were more intelligent than blacks, native-born Americans were more intelligent than immigrants, and northern Europeans were more intelligent than southern Europeans. Educational psychologists believed IQ tests measured innate intelligence, but mostly they measured knowledge of white American culture and language. This underestimated the intelligence of new immigrants and disenfranchised Americans.
Para saber más de esta ida de pinza, visita el Eugenicsarchive. Atención a lo que llevaban las ideas del polímata Galton.
Cómo es algo difícil de navegar la página, aquí os dejo el archivo de imágenes.
No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario